Introduction
India is among one of the leading countries that are moving towards a cashless economy. With 89.5 million digital transactions in 2022, India is among the top five countries in digital payments.
India accounted for 46% of the global real-time payments, and the digital transactions in India were more than the four countries combined in 2022. Let’s understand more about digital payments in India, the importance of government initiatives, overcoming challenges, and staying ahead of future trends. (Source: TOI)
Unleashing the Power of Digital Transactions
India’s Payment Landscape transformation in digital payments is driven by three key factors: government initiatives, technology advancements, and smartphone penetration.
The Indian government’s initiatives, such as Digital India and DigiDhan Abhiyan, have promoted digital transactions and financial inclusion. Technological advancements, particularly the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), have revolutionized payments in India. UPI’s user-friendly interface and interoperability have made it easier for people to make instant transactions across banks and payment providers.
Increased smartphone penetration and internet connectivity have made digital payments more accessible to a broader population. Affordable smartphones and data plans have empowered consumers to use mobile wallets and payment apps conveniently, reducing reliance on physical cash.
Transforming Payments: UPI’s Simple and Impactful Revolution
The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has revolutionized India’s payment landscape by simplifying digital transactions. UPI, as an instant payment system, enables seamless fund transfers between bank accounts through mobile platforms. Its impact has been widespread and transformative.
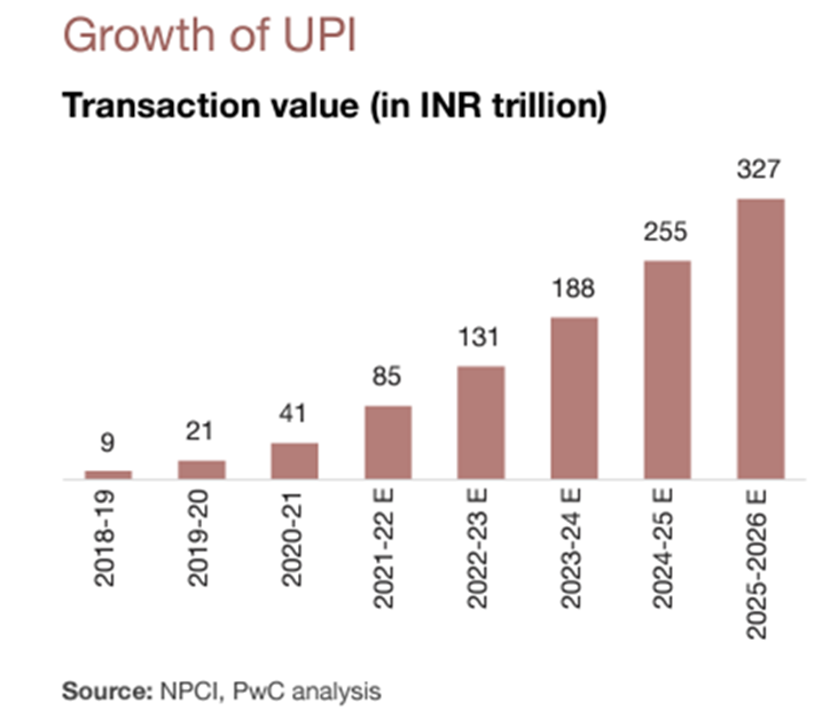
The key benefits of UPI lie in its simplicity and convenience. With UPI, users can make 24/7 payments without needing bank account details or multiple payment apps. It ensures security through a unique Virtual Payment Address (VPA) and two-factor authentication. UPI also provides flexibility by allowing users to link multiple bank accounts, offering a seamless and personalized payment experience.
UPI’s role in driving digital transactions is significant. It has been instrumental in promoting financial inclusion, especially among the unbanked population. UPI facilitates person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) payments, bill payments, and government transactions. Its user-friendly interface and interoperability have made it compatible with various service providers, merchants, and applications.
The Increasing Acceptance of Digital Transactions in India
Over the past five years, India has witnessed significant growth in easy and convenient digital payment modes. Bharat Interface for Money-Unified Payments Interface (BHIM-UPI), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), and National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) have played a pivotal role in transforming the digital payment ecosystem.
These modes have facilitated a surge in person-to-person (P2P) and person-to-merchant (P2M) payments. Notably, BHIM UPI has emerged as the preferred payment method among citizens, with an impressive 803.6 crore digital payment transactions valued at ₹12.98 lakh crore recorded in January 2023.
The following figures represent the total count of digital payment transactions carried out in the past five financial years and the ongoing financial year:
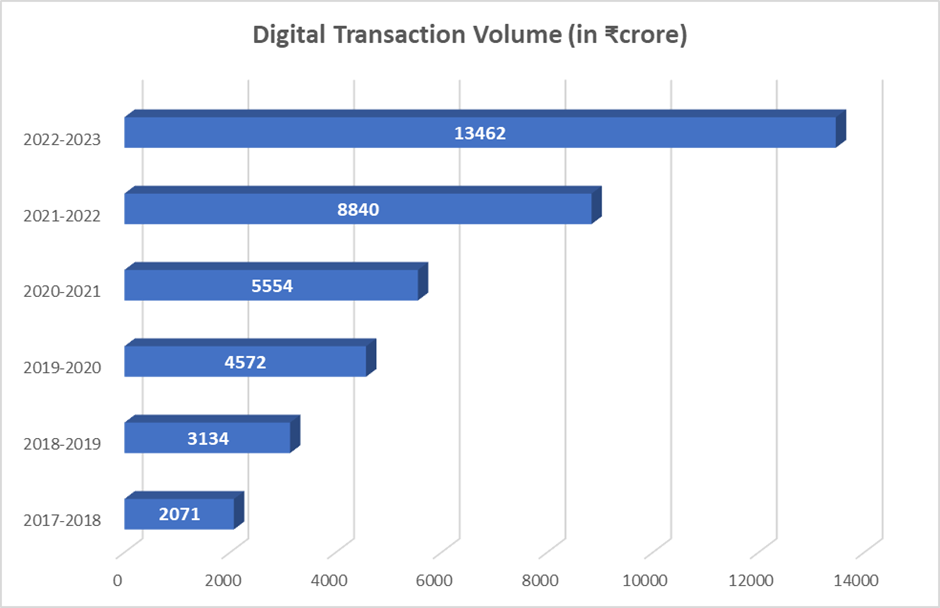
The following numbers depict the cumulative value of digital payments in the preceding five financial years and the current financial year:
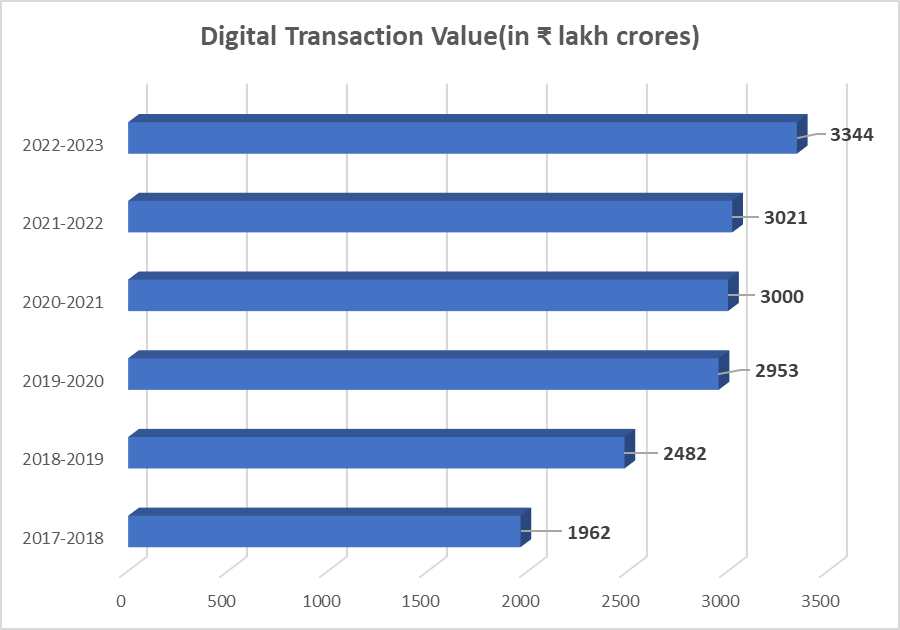
Key Players Transforming India’s Digital Payments
Prominent payment platforms like UPI, Paytm, PhonePe, and Google Pay have revolutionized digital transactions, offering user-friendly interfaces for easy payments and transfers. The graph below illustrates the UPI transactions of major players up until March 2023.
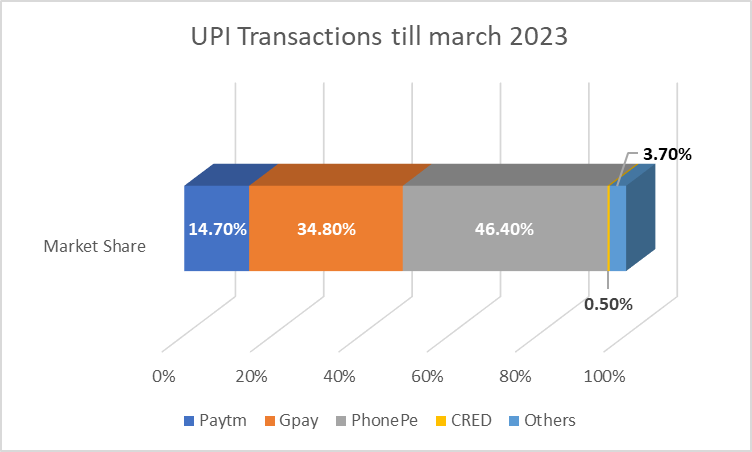
Payment banks have played a vital role in facilitating digital transactions and promoting financial inclusion. With simplified account opening processes and mobile banking apps, payment banks have made digital payments accessible to underserved sections of the population.
Fintech companies have also significantly contributed by leveraging technology to provide innovative solutions. Their payment processing systems, digital wallets, and peer-to-peer transfers have streamlined digital transactions, making them faster and more convenient.
Advantages of Digital Payments in India’s Payment Landscape
- Convenience: Digital payments offer a user-friendly and convenient way to transact, eliminating the need for physical cash or bank visits.
- Security: Advanced security measures like encryption and two-factor authentication ensure safe and secure transactions.
- Financial Inclusion: Digital payments provide access to banking services for the unbanked, bridging the urban-rural divide.
- Speed and Efficiency: Quick and seamless transactions save time by eliminating the hassle of cash handling.
- Transparency: Transparent records enable easy tracking and management of finances for individuals and businesses.
- Contactless Transactions: Promote hygiene and reduce the spread of germs through contactless payment methods.
- Integration: Integration with other services creates a comprehensive financial ecosystem, including bill payments and online shopping.
- Cost Savings: Digital payments save physical cash handling and transportation costs.
- Sustainability: Reduce paper usage, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Accessibility: Accessible to users with limited mobility or geographical constraints, promoting inclusivity.
Final Words
India’s Payment Landscape is undergoing a significant transformation fueled by the increasing adoption of digital payments. Government initiatives, technological advancements, and smartphone penetration have played vital roles in driving this evolution. The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has emerged as a game-changer, simplifying transactions and promoting financial inclusion. The advantages of digital payments, including convenience, security, and financial inclusion, further contribute to the growing popularity and integration of digital payments in India’s Payment Landscape.
FAQs
What is Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY)?
Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is a government-backed financial inclusion program launched in India in 2014. PMJDY aims to provide access to financial services such as bank accounts, savings accounts, insurance, and credit to society’s poor and marginalized sections.
What was the impact of demonetization on digital payments?
Demonetization had a significant impact on digital payments in India. In the months following the announcement, there was a sharp increase in the use of digital payment methods such as mobile wallets, online banking, and UPI. People were looking for ways to pay for goods and services without cash.
Why is digital literacy and awareness important for digital payments?
Digital literacy and awareness are essential for digital payments because they help people understand how to use them safely and securely. They also help people understand digital payments’ potential benefits and risks.
How can digital literacy and awareness be promoted?
To promote digital literacy and awareness, various methods can be employed, such as:
● Education and training programs
● Public awareness campaigns
● The development of resources and tools
Read more: How Long-term investing helps create life-changing wealth – TOI.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 4 / 5. Vote count: 9
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.