Introduction
In 2004, India introduced the Securities Transaction Tax (STT) as a replacement for the erstwhile “stamp duty” on securities transactions. This tax serves a dual purpose: it acts as a significant source of government revenue and, crucially, serves as a deterrent against speculative trading by increasing the associated costs.
The Need for STT
The initiative behind introducing STT was to curb the evasion of capital gains tax on profits earned from securities transactions. This tax regime was designed to bring greater transparency and accountability to the financial markets.
Impressive Revenue Performance
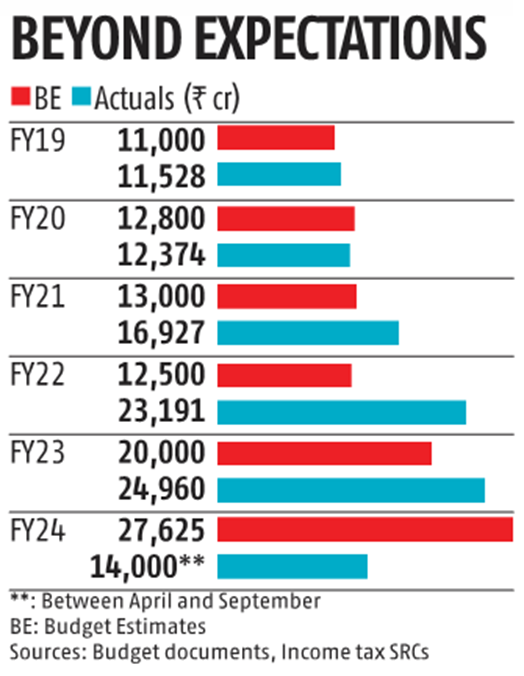
The revenue generated from STT for the central government has shown remarkable performance, exceeding 50 percent of the annual estimate for FY24. In concrete terms, approximately Rs 14,000 crore has been collected in the first half of the fiscal year, compared to a full-year target of Rs 27,625 crore for 2023-24.
Key Contributors to Revenue Growth
Several factors have contributed to this impressive collection:
- Robust Equity Markets: The stability and growth of the equity markets have created a conducive environment for trading.
- Increased Derivative Transactions: The surge in transactions in derivatives has further fueled the growth of STT revenue.
- An influx of New Investors: Adding new investors to the market has played a pivotal role in enhancing overall trading activity.
STT’s Role in Government Revenue
While the STT contributes to the government’s revenue, it is not yet substantial enough to significantly impact the overall revenue.
The Securities Transaction Tax in India has proven to be effective in generating government revenue and discouraging speculative trading. Its role in curbing tax evasion and promoting market transparency cannot be overstated. As India’s financial markets evolve, the STT is expected to play an increasingly pivotal role.
FAQs
What is the purpose of the Securities Transaction Tax (STT)?
The primary purpose of the STT is twofold: it serves as a source of government revenue and acts as a deterrent against speculative trading.
How has the STT performed in terms of revenue collection?
The STT has exceeded 50 percent of the annual estimate for FY24, with approximately Rs 14,000 crore collected in the first half of the fiscal year.
Is the STT a substantial contributor to the government’s overall revenue?
While the STT plays a significant role in government revenue, it is not yet substantial enough to significantly impact the overall revenue.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
 Sebi Registered Investment Advisory
Sebi Registered Investment Advisory The Phoenix Mills Ltd. (PDF)
The Phoenix Mills Ltd. (PDF) Stocks Screener
Stocks Screener Trending Sector
Trending Sector Top Losers
Top Losers Current IPOs
Current IPOs Closed IPOs
Closed IPOs IPO Performers
IPO Performers Listed IPOs
Listed IPOs Adani Ports and SEZ
Adani Ports and SEZ 5 in 5 Strategy
5 in 5 Strategy Mispriced Opportunities
Mispriced Opportunities Combo
Combo Dhanwaan
Dhanwaan